Optometry EHR Software: A Complete Guide to Features, Benefits, and AI Innovation in 2026

Introduction: Why Optometry EHR Software Is Now Essential
Electronic Health Record (EHR) software has become a core operational system for optometry practices. What began as a digital replacement for paper charts has evolved into an integrated platform that supports clinical documentation, scheduling, billing, compliance, analytics, and patient engagement.
According to the Office of the National Coordinator for Health IT (https://www.healthit.gov/faq/what-are-advantages-electronic-health-records), EHR systems improve access to patient information, reduce errors, and support better coordination of care across healthcare settings. As adoption has become nearly universal across U.S. healthcare, optometry practices that rely on outdated or non-specialized systems face growing operational and competitive disadvantages.
Optometry-specific EHR software is designed to support eye-care workflows such as refraction documentation, contact lens management, diagnostic imaging integration, and vision insurance billing. As regulatory expectations increase and patient demand for digital convenience grows, modern EHR systems have become essential infrastructure for sustainable optometric practice.
Core Features of Optometry EHR Software
Patient Records and Chart Management
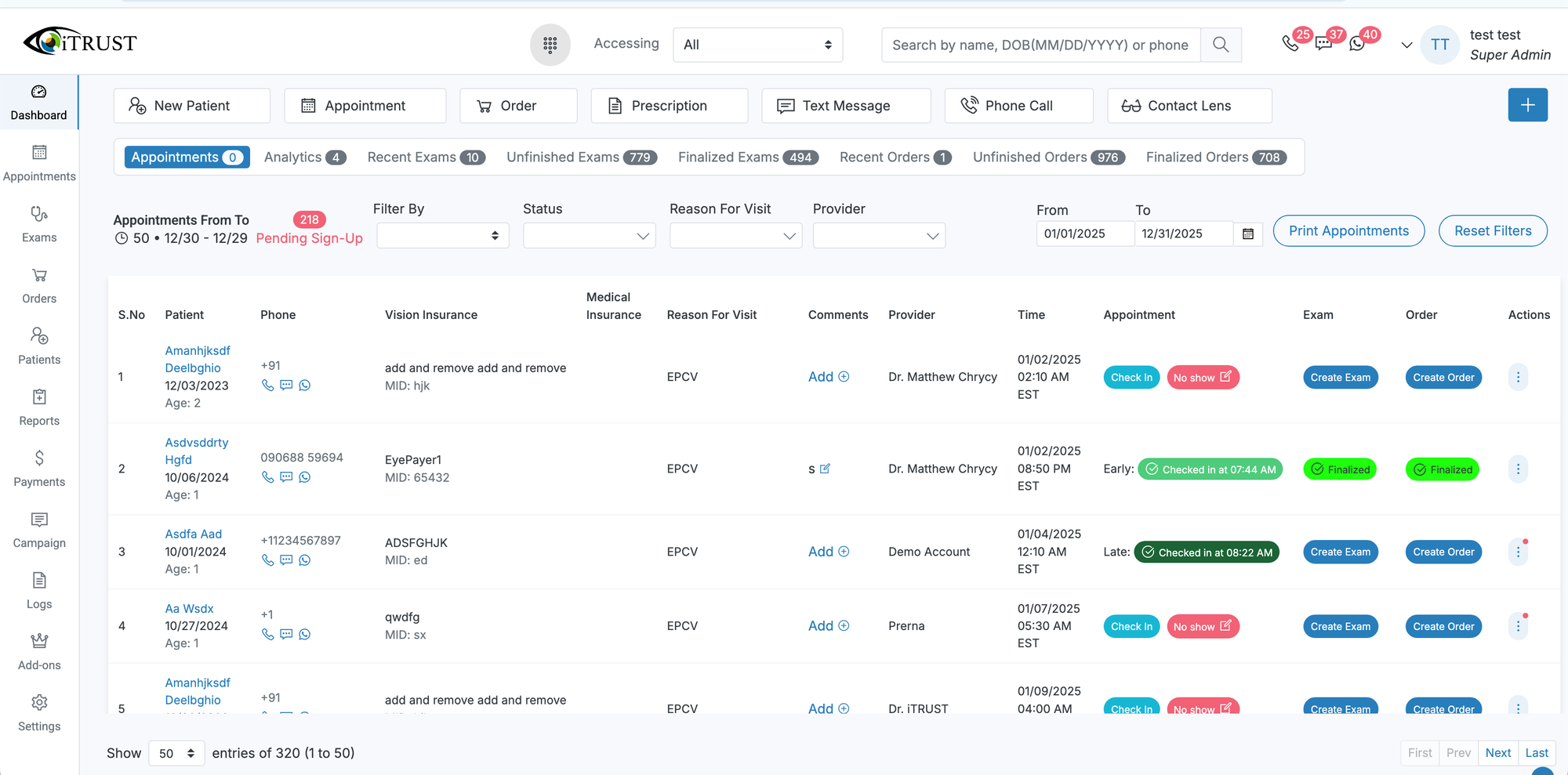
At the foundation of optometry EHR software is the secure digital patient record. These records consolidate demographics, ocular and medical history, prescriptions, exam findings, diagnostic images, and treatment plans into a longitudinal chart that follows the patient over time.
Centralized digital records reduce clinical errors and improve continuity of care, a benefit supported by national findings published through the National Institutes of Health at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5368202/. Optometry EHR platforms typically include structured ocular history fields, secure document storage, electronic prescribing, and patient portals that allow patients to complete intake forms and access visit information online.
Optometry-Specific Exam Documentation
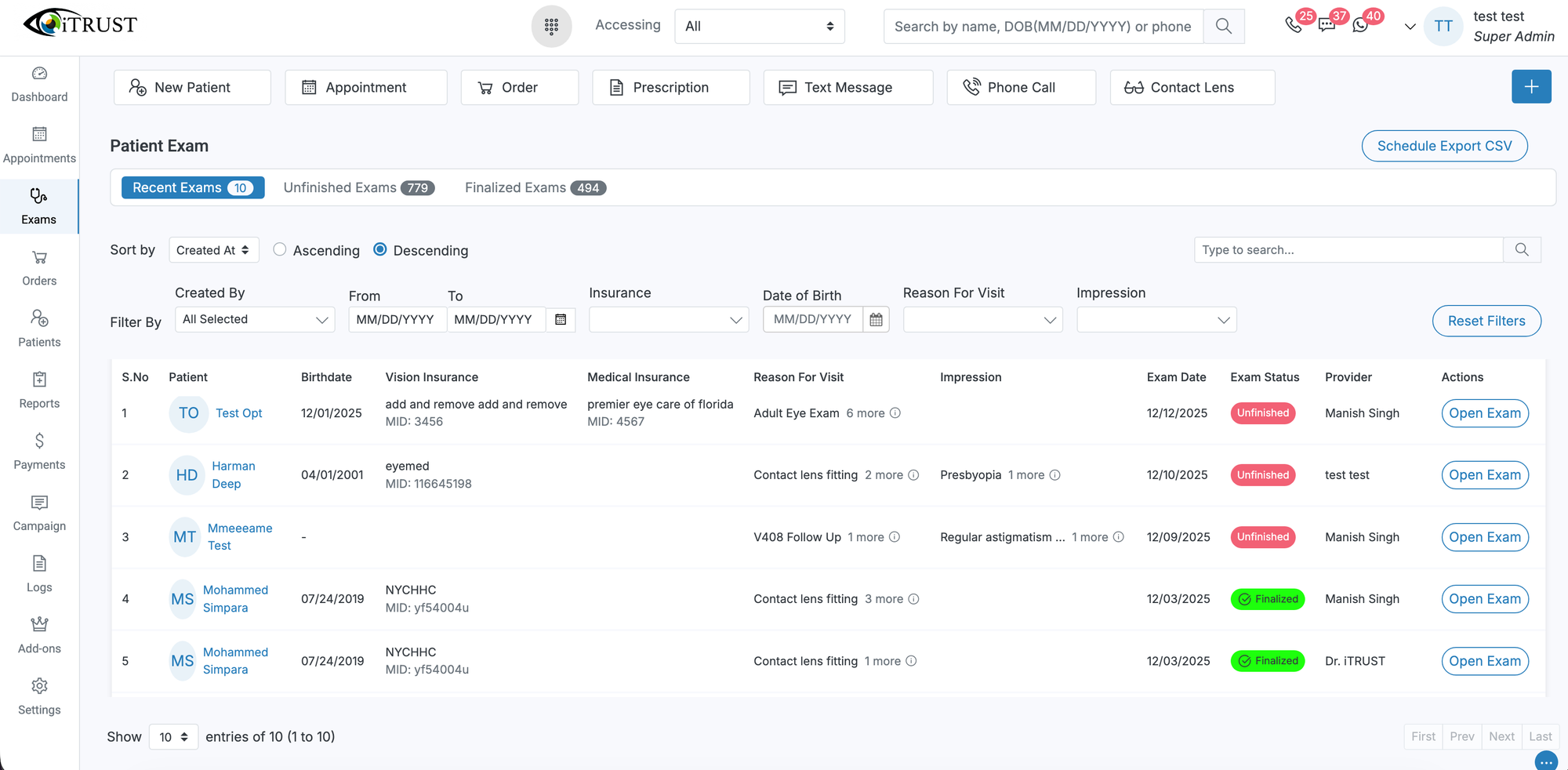
Unlike generic medical EHRs, optometry platforms include exam templates built specifically for eye care. Providers can document visual acuity, refraction results, slit lamp findings, tonometry readings, and retinal evaluations using structured fields and diagram-based tools.
Many systems integrate directly with diagnostic devices such as OCT scanners, fundus cameras, and visual field analyzers, enabling automated import of results into the patient chart. Centralizing diagnostic data supports longitudinal disease tracking and improves clinical decision-making, particularly for chronic conditions such as glaucoma and diabetic eye disease.
HealthIT.gov emphasizes that standardized digital documentation and interoperability improve workflow efficiency and reduce ambiguity across providers, as outlined at https://www.healthit.gov/topic/health-it-and-health-information-exchange-basics/interoperability.
Scheduling and Appointment Management
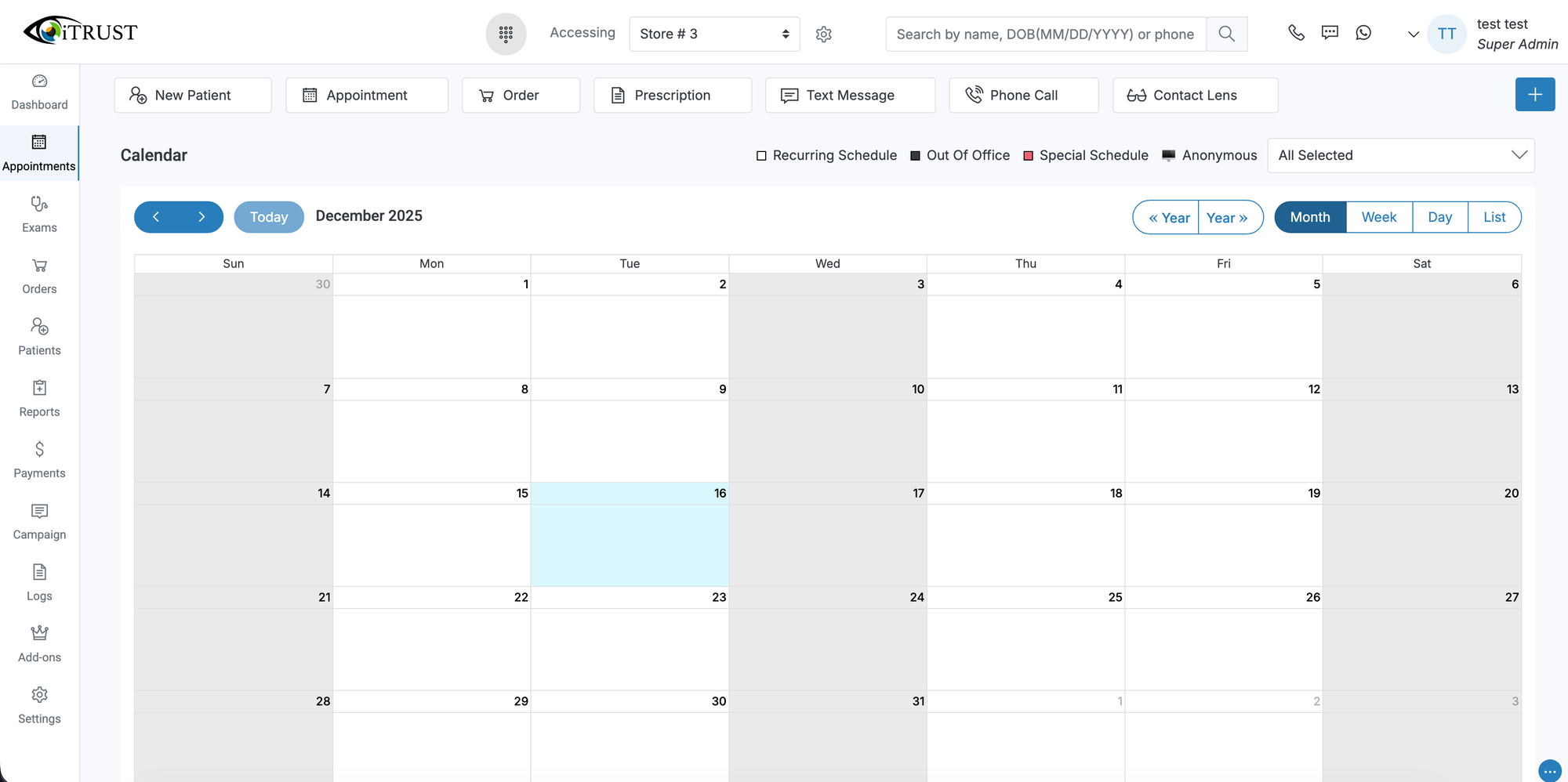
Scheduling tools are a core component of optometry EHR software. Integrated calendars allow practices to manage multiple providers, appointment types, and locations within a single system. Automated appointment reminders delivered via text or email help reduce no-show rates and improve patient engagement.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services notes that EHR-enabled scheduling and communication tools contribute to improved care delivery and operational efficiency, as discussed at https://www.cms.gov/research-statistics-data-and-systems.
Online self-scheduling and recall systems further enhance accessibility, allowing patients to book appointments and receive reminders without placing additional strain on front-desk staff.
Billing, Claims, and Revenue Cycle Management
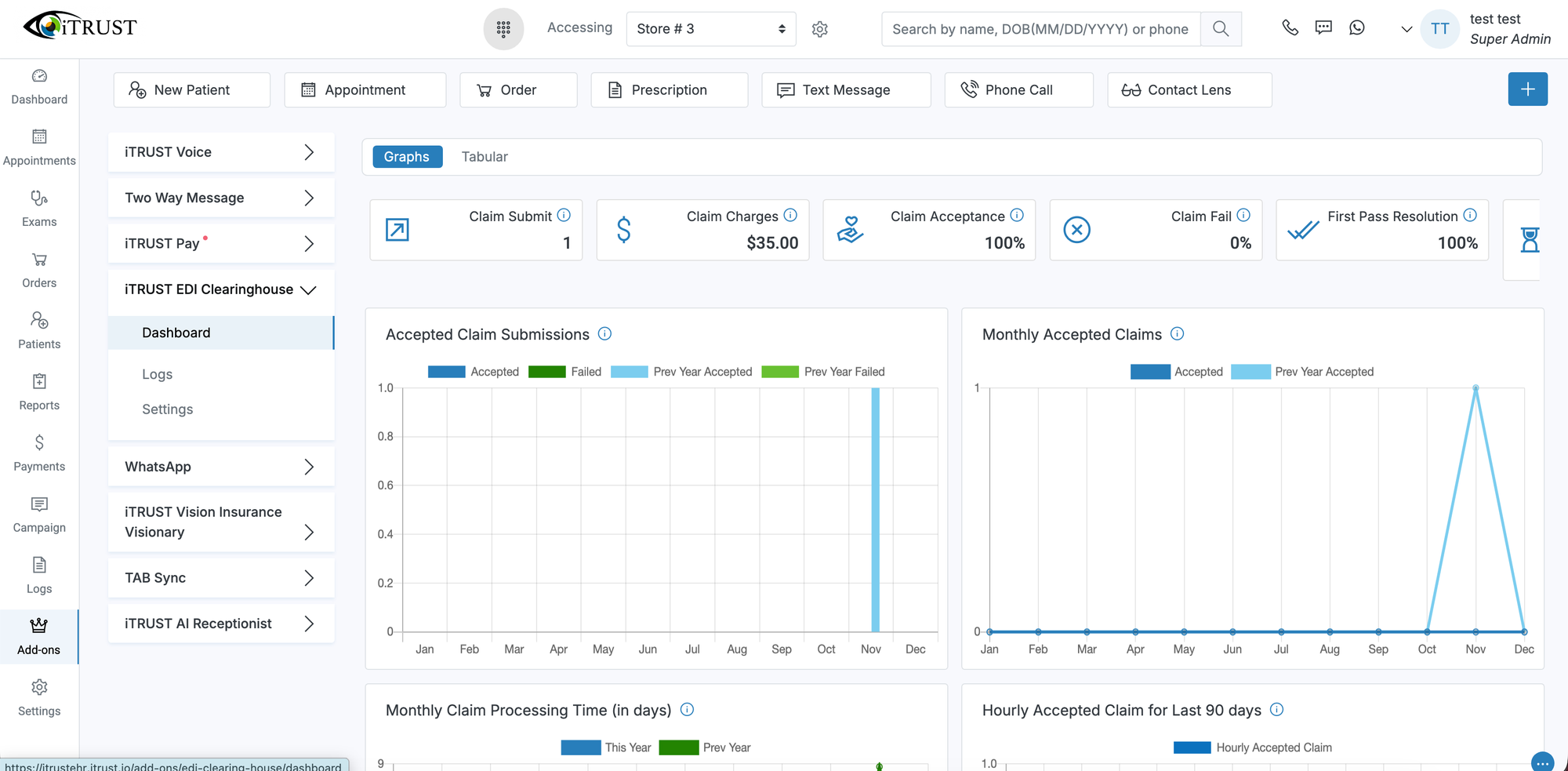
Optometry billing is uniquely complex due to the overlap of medical and vision insurance. Optometry EHR software simplifies this process by linking clinical documentation directly to billing workflows, ensuring accurate charge capture and coding.
Integrated billing features include support for medical and vision claims, CPT and ICD-10 coding assistance, electronic claims submission, and reimbursement tracking. Research from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality shows that EHR adoption can produce significant financial benefits by reducing billing errors and administrative waste, as detailed at https://digital.ahrq.gov/ahrq-funded-projects/evaluation-costs-and-benefits-health-information-technology.
Reporting and Analytics
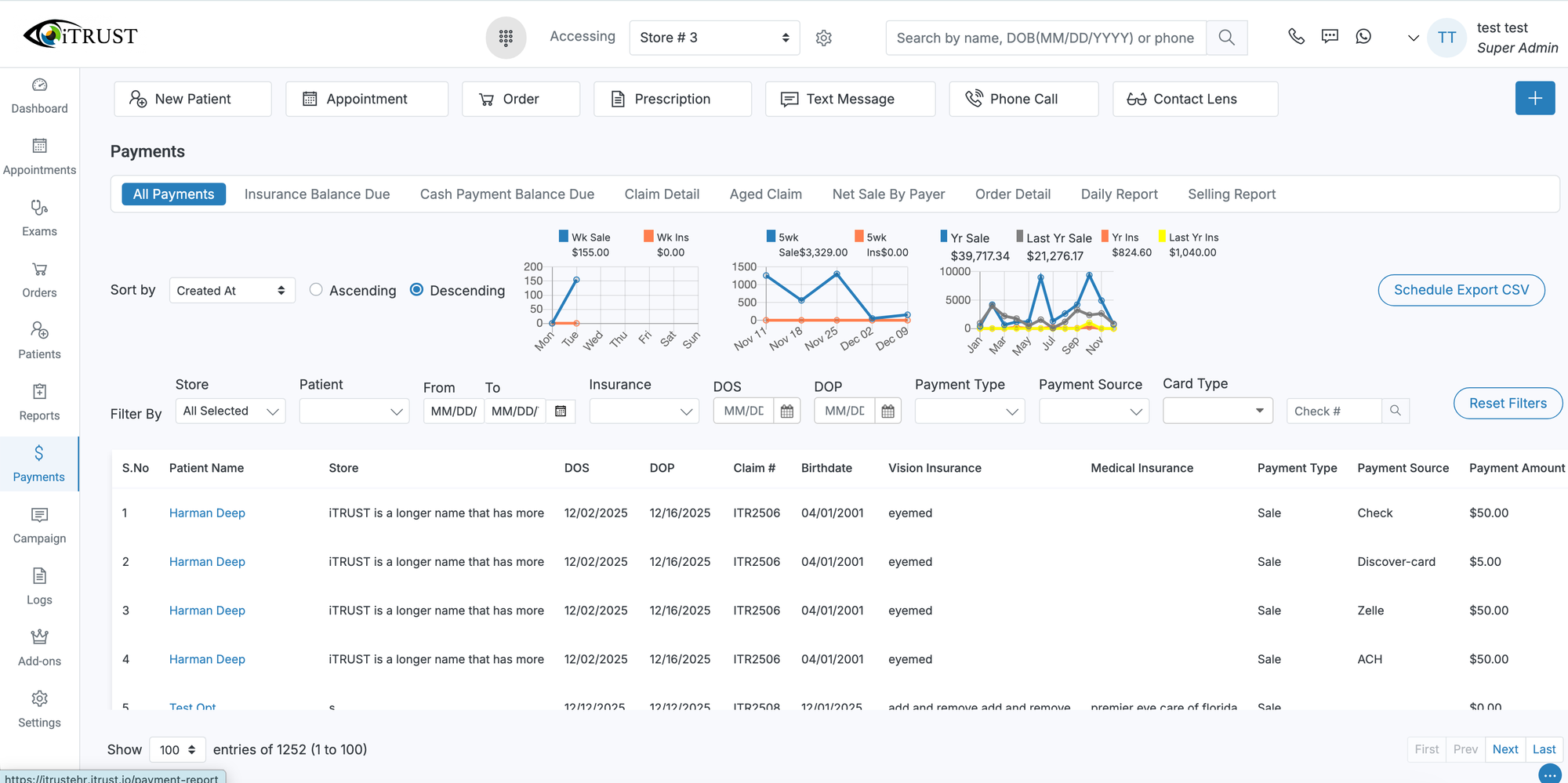
Modern optometry EHR platforms include reporting and analytics tools that provide insight into both clinical and business performance. Practices can track patient volume, no-show rates, revenue by service type, and optical inventory trends.
On the clinical side, structured EHR data supports quality reporting and population health analysis. National studies published through the NIH indicate that practices using EHR analytics are better equipped to identify care gaps and improve outcomes over time (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5368202/).
Cloud-Based Architecture and Interoperability
Cloud-based optometry EHR software has become the industry standard. Cloud platforms reduce IT overhead, enable automatic updates, and allow secure access from multiple locations. This architecture also improves disaster recovery and long-term scalability.
Interoperability is a critical component of modern EHR systems. Certified platforms support data exchange standards such as HL7 and FHIR, enabling secure information sharing between optometrists, primary care providers, specialists, and health information exchanges. HealthIT.gov highlights the importance of interoperable EHR systems for improving care coordination and workflow efficiency at https://www.healthit.gov/topic/health-it-and-health-information-exchange-basics/interoperability.
Artificial Intelligence in Optometry EHR Software
AI-Assisted Clinical Documentation
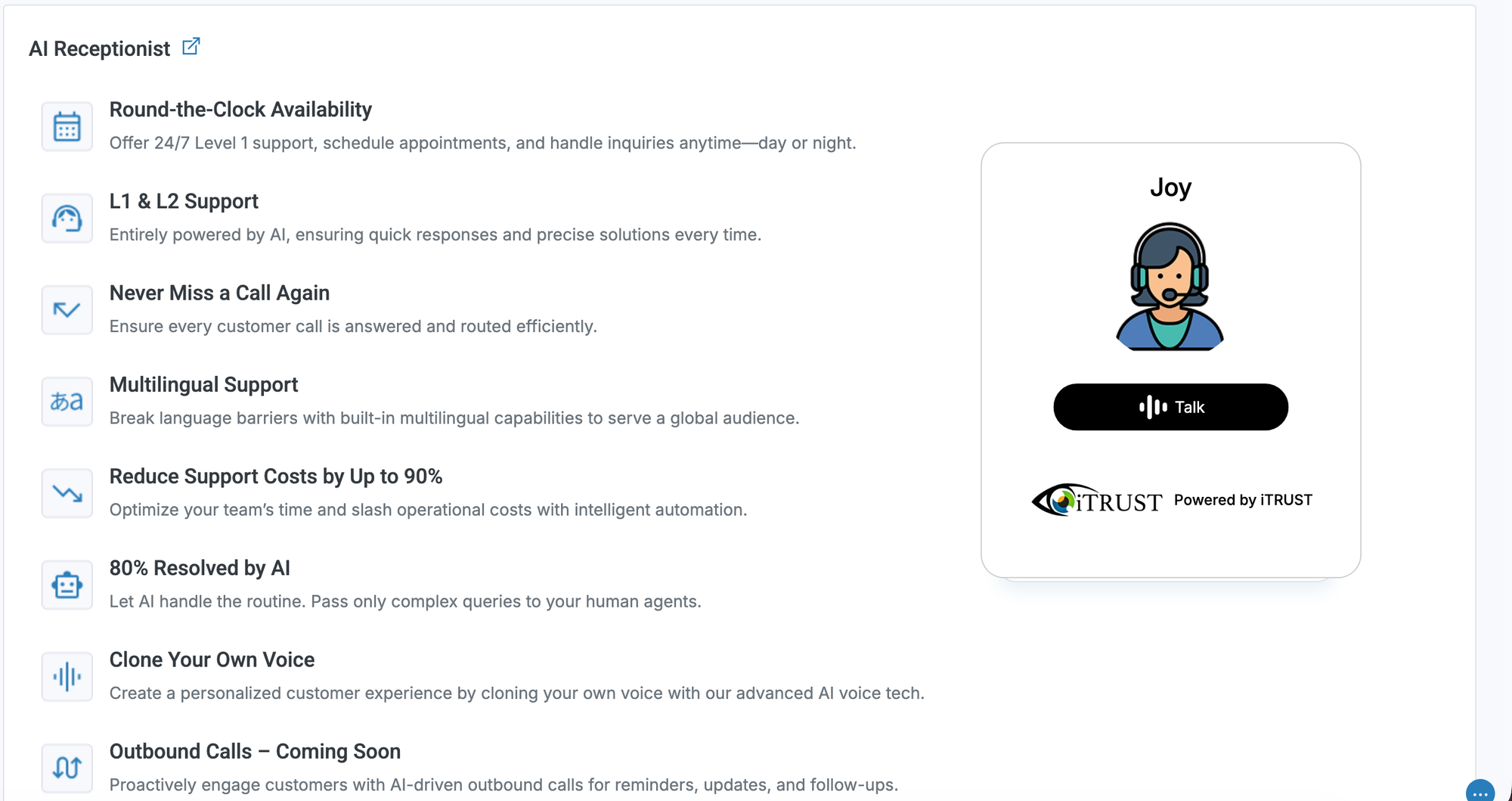
Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming EHR functionality. AI-assisted documentation tools analyze provider inputs and exam data to generate structured clinical notes, reducing time spent on charting.
Research from the University of North Carolina’s Kenan Institute of Private Enterprise demonstrates that AI documentation tools can save clinicians several hours per week while maintaining accuracy and quality (https://kenaninstitute.unc.edu/research/ai-integration-and-its-impact-on-clinical-labor/). In optometry, AI tools can assist with identifying abnormal trends, supporting coding accuracy, and streamlining exam workflows.
AI-Driven Patient Communication
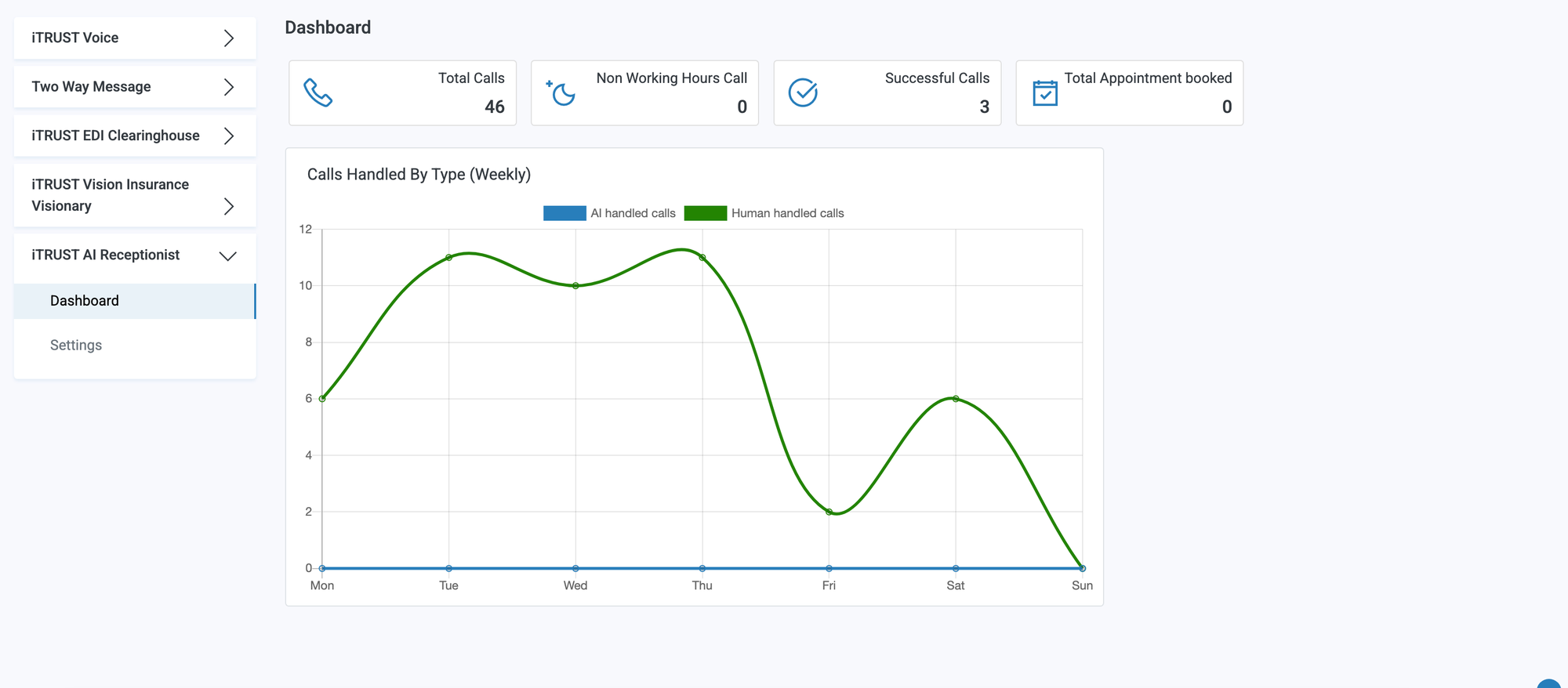
AI is also being used to automate routine patient communication within EHR platforms. Common inquiries related to appointments, prescriptions, and office hours can be handled automatically, improving response times and reducing staff workload.
The American Medical Association reports that AI-enabled administrative tools play a growing role in reducing physician and staff burnout, as outlined at https://www.ama-assn.org/practice-management/digital/how-ai-helping-reduce-physician-burnout.
Benefits of Optometry EHR Software
Improved Efficiency and Productivity
By streamlining documentation, scheduling, and billing, EHR software reduces administrative burden and allows providers to focus more on patient care. National surveys consistently show that most clinicians believe EHRs improve care quality and operational efficiency, according to NIH findings at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5368202/.
Enhanced Patient Experience
Optometry EHR systems improve the patient experience by enabling faster check-ins, clearer communication, and coordinated care. Patient portals allow individuals to access prescriptions, exam history, and appointment scheduling online, increasing engagement and satisfaction.
Data Security and Regulatory Compliance
Protecting patient health information is a legal and ethical requirement. EHR systems support compliance with the HIPAA Security Rule through encryption, access controls, audit logs, and secure data storage.

The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services outlines national standards for protecting electronic health information at https://www.hhs.gov/hipaa/for-professionals/security/laws-regulations/index.html, noting that electronic safeguards significantly reduce risks compared to paper-based systems.
Improved Practice Management and Decision-Making
Integrated dashboards and analytics provide practice owners with real-time visibility into operations. This supports informed decisions related to staffing, scheduling, marketing, and long-term growth.
iTRUST EHR: Advancing AI-Powered Optometry Software
iTRUST EHR represents the next generation of optometry-specific EHR platforms. Built as a cloud-based system, iTRUST integrates clinical documentation, scheduling, billing, inventory management, and analytics into a unified environment.
iTRUST’s AI-powered tools assist with exam documentation and patient communication, aligning with broader healthcare trends that emphasize automation and efficiency as outlined by the University of North Carolina and the American Medical Association (https://kenaninstitute.unc.edu/research/ai-integration-and-its-impact-on-clinical-labor/ and https://www.ama-assn.org/practice-management/digital/how-ai-helping-reduce-physician-burnout).
Conclusion
Optometry EHR software has become essential for delivering efficient, secure, and high-quality eye care. By integrating clinical documentation, billing, scheduling, analytics, and AI-driven automation, modern EHR platforms enable practices to operate more effectively while improving patient outcomes.
As healthcare continues to embrace digital transformation, optometry practices that adopt advanced, cloud-based, AI-enabled EHR systems will be better positioned to meet regulatory requirements, patient expectations, and long-term growth objectives.
References
- Office of the National Coordinator for Health IT
https://www.healthit.gov/faq/what-are-advantages-electronic-health-records - U.S. Department of Health & Human Services – HIPAA Security Rule
https://www.hhs.gov/hipaa/for-professionals/security/laws-regulations/index.html - National Institutes of Health – Clinical Benefits of EHR Use
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5368202/ - HealthIT.gov – Interoperability
https://www.healthit.gov/topic/health-it-and-health-information-exchange-basics/interoperability - Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services – EHRs and Quality
https://www.cms.gov/research-statistics-data-and-systems - Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality – Costs and Benefits of Health IT
https://digital.ahrq.gov/ahrq-funded-projects/evaluation-costs-and-benefits-health-information-technology - Kenan Institute, University of North Carolina – AI in Clinical Labor
https://kenaninstitute.unc.edu/research/ai-integration-and-its-impact-on-clinical-labor/ - American Medical Association – AI and Burnout Reduction
https://www.ama-assn.org/practice-management/digital/how-ai-helping-reduce-physician-burnout - Harvard Medical School – EHRs and Quality of Care
https://hms.harvard.edu/news/electronic-health-records-and-quality-care - World Health Organization – Digital Health
https://www.who.int/health-topics/digital-health